To set up the tunnel, you’ll need to perform the following high-level steps:
- Create a server configuration on Intune.
- Create a site in Intune.
- Install a Microsoft Tunnel Gateway on a Linux server in your on-premises environment (by using an Intune script).
- Deploy the Microsoft Tunnel client app to your iOS and Android devices.
- Create and deploy VPN profiles to your iOS and Android devices.
Specifically, you’ll use Intune to perform the following:
• Download the Microsoft Tunnel installation script which you must run on your Linux container
• Configure aspects of Microsoft Tunnel Gateway: IP addresses, DNS servers, and ports
• Deploy VPN profiles to devices
• Deploy the Microsoft Tunnel client apps
Create the Server Configurations
Let’s examine the process. We start by creating server configurations: - Open Microsoft Intune admin center.
- In the navigation pane, select Tenant administration.
- On the Tenant admin | Tenant status page, select Microsoft Tunnel Gateway.
- Click the Server configurations tile on the Tenant admin | Microsoft Tunnel Gateway page, as shown in Figure 3-33.
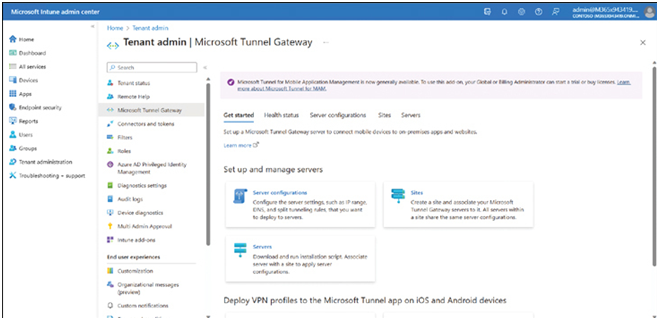
FIGURE 3-33 Provisioning the Microsoft Tunnel Gateway
- Click Create new.
- On the Create server configuration page, on the Basics tab, enter a Name and Description and click Next.
- On the Settings page, displayed in Figure 3-34, enter the following information and click Next:
• IP address range The addresses provided to Android and iOS devices when they connect through the tunnel.
• Server port The listening TCP port used by your server. Typically, this will be 443.
• DNS servers The IP addresses of DNS servers that are used by the remote client devices.
• DNS suffix search The DNS suffix applied to the client devices for DNS searches.
• Split tunneling rules Determine how IP routing is handled through the tunnel.
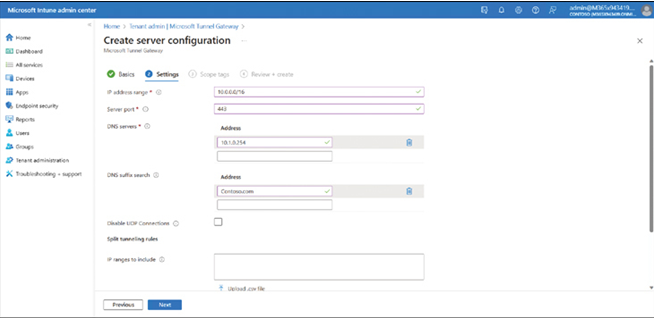
FIGURE 3-34 Creating the server configuration
- On the Scope tags page, define any tags and click Next.
- On the Review + create page, click Create.


